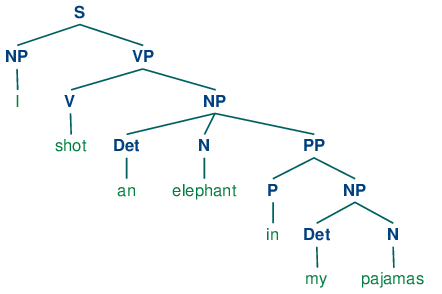
How to Analyze Grammatically as a Sentence
To analyze grammatically as a sentence means to identify the syntactic, morphological, and semantic components that make a sentence complete and coherent. Grammar analysis divides a sentence into subject, predicate, objects, complements, modifiers, and connectors. Linguists use grammatical analysis to determine how words function and relate to each other under the rules of syntax and morphology.
Understanding Grammatical Analysis
Grammatical analysis examines how words combine to form meaningful expressions. It studies the arrangement of phrases, agreement between elements, and the role each component plays.
Every sentence follows a hierarchical structure, where clauses and phrases build meaning through grammatical dependencies.
| Element | Function | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject | Performs action | John runs fast. | “John” is the subject doing the action. |
| Predicate | Expresses action/state | John runs fast. | “Runs fast” tells what John does. |
| Object | Receives action | John reads books. | “Books” receives the action of reading. |
| Complement | Adds detail | She is happy. | “Happy” describes the subject. |
| Modifier | Adds description | The red car moved. | “Red” modifies “car.” |
Identify the Sentence Structure
To analyze grammatically as a sentence, begin by identifying the sentence structure.
English has four primary sentence types:
-
Simple Sentence – contains one independent clause.
Example: The dog barked. -
Compound Sentence – contains two independent clauses joined by a conjunction.
Example: The dog barked, and the cat ran. -
Complex Sentence – contains an independent clause and at least one dependent clause.
Example: The dog barked when it saw the stranger. -
Compound-Complex Sentence – combines two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses.
Example: The dog barked when it saw the stranger, and the cat hid.
Each type serves a distinct function in communication. The complexity increases as clauses combine.
Determine the Parts of Speech
To analyze grammatically as a sentence, determine the part of speech of each word.
English has eight major parts of speech, each serving a structural role.
| Part of Speech | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Noun | Names a person, place, thing, or idea | teacher, river |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | she, they |
| Verb | Expresses action or state | run, is |
| Adjective | Describes a noun | blue, tall |
| Adverb | Modifies verb/adjective/adverb | quickly, very |
| Preposition | Shows relation | in, under |
| Conjunction | Joins words/phrases/clauses | and, but |
| Interjection | Expresses emotion | oh!, wow! |
Recognizing the grammatical role clarifies sentence balance and function.
Examine Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement ensures that the verb form matches the subject in number and person.
Grammar analysis identifies mismatches that affect grammatical accuracy.
Examples:
-
Correct: She writes every day.
-
Incorrect: She write every day.
Verbs adjust to singular or plural subjects. Auxiliary verbs follow similar patterns:
He has gone (singular), They have gone (plural).
Understand Clause Functions
Clauses are building blocks of sentences. Each contains a subject and a predicate.
-
Independent Clause: Expresses a complete thought.
The sun rises in the east. -
Dependent Clause: Cannot stand alone; requires an independent clause.
When the sun rises, the city awakens.
Dependent clauses function as adjectives, adverbs, or nouns. Identifying their role defines grammatical precision.
Analyze Phrase Composition
A phrase is a group of words acting as a unit but lacking a full clause structure. Common types include:
-
Noun Phrase: A group centered around a noun.
The tall building. -
Verb Phrase: A main verb with auxiliaries.
Has been running. -
Adjective Phrase: Modifies a noun.
Very bright and beautiful. -
Adverbial Phrase: Modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
In a hurry. -
Prepositional Phrase: Begins with a preposition.
On the table.
Analyzing these reveals semantic layers within the sentence.
Study the Sentence Pattern
Grammar analysis categorizes sentences into patterns based on their functional structure.
According to traditional English grammar, there are seven core sentence patterns:
-
Subject + Verb (SV) – Birds fly.
-
Subject + Verb + Object (SVO) – Dogs chase cats.
-
Subject + Verb + Complement (SVC) – He is happy.
-
Subject + Verb + Indirect Object + Direct Object (SVIDO) – She gave him a book.
-
Subject + Verb + Object + Complement (SVOC) – They made him leader.
-
Intransitive Pattern – It rains.
-
Transitive Pattern – He plays football.
Each pattern provides a predictable syntactic framework used in analysis.
Determine the Function of Words
Every word in a sentence holds a grammatical function. Identifying function ensures syntactic clarity.
| Word | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| The | Determiner | Specifies a noun |
| Boy | Subject | Performs action |
| Quickly | Adverb | Describes verb |
| Ran | Verb | Expresses action |
| Home | Noun | Object of movement |
Functional analysis prevents ambiguity in interpretation.
Examine Tense and Aspect
Tense expresses time, while aspect shows the nature of action.
English uses twelve main tenses across three aspects: simple, continuous, and perfect.
Examples:
-
Simple Present: She writes.
-
Present Continuous: She is writing.
-
Present Perfect: She has written.
-
Past Continuous: She was writing.
Tense analysis identifies temporal relationships in grammar.
Evaluate Voice and Mood
Voice shows whether the subject acts or receives action.
Mood expresses the attitude of the speaker.
Active Voice: The teacher explained the lesson.
Passive Voice: The lesson was explained by the teacher.
Indicative Mood: States facts.
Imperative Mood: Issues commands.
Subjunctive Mood: Expresses wishes or hypotheticals.
Assess Sentence Cohesion and Coherence
Cohesion links words through grammatical connectors like conjunctions, pronouns, and determiners.
Coherence ensures logical flow between ideas.
To analyze grammatically as a sentence, both cohesion and coherence must align.
Example:
He opened the door because he heard a noise.
The conjunction because connects cause and effect logically.
Common Grammatical Analysis Methods
Several linguistic methods exist for sentence analysis:
-
Traditional Grammar – Focuses on rules and syntax categories.
-
Structural Grammar – Studies patterns and positions.
-
Transformational Grammar – Examines deep structure and meaning transformation.
-
Dependency Grammar – Identifies hierarchical relationships between words.
-
Systemic Functional Grammar – Explores how grammar constructs meaning in context.
Each method provides a different linguistic lens for analyzing sentences.
See More: Accounts Payable Approval Process: The Definitive 2025 Guide to Streamlined Invoice Management
Step-by-Step Method to Analyze a Sentence Grammatically
-
Identify the subject and predicate.
-
Determine sentence type (simple, compound, complex).
-
Break into clauses and phrases.
-
Label parts of speech.
-
Check subject-verb agreement.
-
Analyze tense and aspect.
-
Identify modifiers and complements.
-
Determine the sentence pattern.
-
Review cohesion and logical order.
Following these steps ensures grammatical accuracy and semantic depth.
See More: MHIC MD: Complete Guide to Maryland Home Improvement Contractor Licensing and Compliance
Key Importance of Grammatical Analysis
Grammatical analysis enhances writing clarity, linguistic understanding, and communication precision.
Educators use it for syntax teaching, translators for structure mapping, and AI models for natural language processing.
Accurate analysis helps in error correction, machine translation, and speech recognition systems.
Tools for Grammatical Sentence Analysis
-
Grammarly – Automated grammar and syntax checking.
-
Parse Tree Generator – Visualizes sentence structure.
-
Syntax Tree Editor – Analyzes phrase relationships.
-
Linguistic Tree Constructor – Models hierarchical dependencies.
-
Stanford Parser – Performs computational syntactic analysis.
-
LanguageTool – Detects stylistic and grammatical errors.
These tools employ linguistic algorithms and NLP models for structural precision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What does “analyze grammatically as a sentence” mean?
It means examining how words function within a sentence according to grammar rules. It involves identifying structure, parts of speech, and syntactic relationships.
Q2. Why is grammatical analysis important?
It improves understanding of sentence formation, prevents writing errors, and enhances clarity in communication.
Q3. What is the first step in grammatical analysis?
Identify the subject and predicate, as they form the foundation of every sentence.
Q4. What tools can analyze grammar effectively?
Professional tools like Grammarly, Stanford Parser, and LanguageTool provide structural and functional insights.
Q5. What is the difference between syntax and grammar?
Syntax is the arrangement of words, while grammar includes all language rules governing structure and usage.
Q6. Can AI analyze grammar accurately?
Modern NLP models can identify syntax and semantics, but linguistic context still requires human validation.
Q7. What are clause and phrase differences?
A clause contains a subject and a verb; a phrase does not but serves as a grammatical unit.
Conclusion
To analyze grammatically as a sentence is to decode the structure, logic, and function that make language meaningful. Every sentence follows an ordered grammatical pattern, where each word serves a specific role governed by syntax and semantics.