Accounts Payable Approval Process: The Definitive 2025 Guide to Streamlined Invoice Management
The accounts payable approval process is the structured workflow a company follows to verify, authorize, and process vendor invoices before releasing payments. It connects procurement, finance, and compliance functions to ensure every outgoing payment is legitimate, accurate, and properly documented.
This process is not only a financial safeguard but also a strategic system for cash flow optimization, supplier trust, and corporate governance.
2. Key Objectives of an Accounts Payable Approval System
| Objective | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Ensures all invoices match purchase orders and delivery receipts. | Reduces duplicate or erroneous payments. |
| Compliance | Aligns with corporate policies and local accounting laws. | Maintains audit readiness. |
| Efficiency | Automates manual verification and approvals. | Decreases processing cycle time. |
| Transparency | Tracks every approval decision in the audit trail. | Builds accountability. |
| Fraud Prevention | Segregates duties and verifies supplier credentials. | Protects against internal and external fraud. |
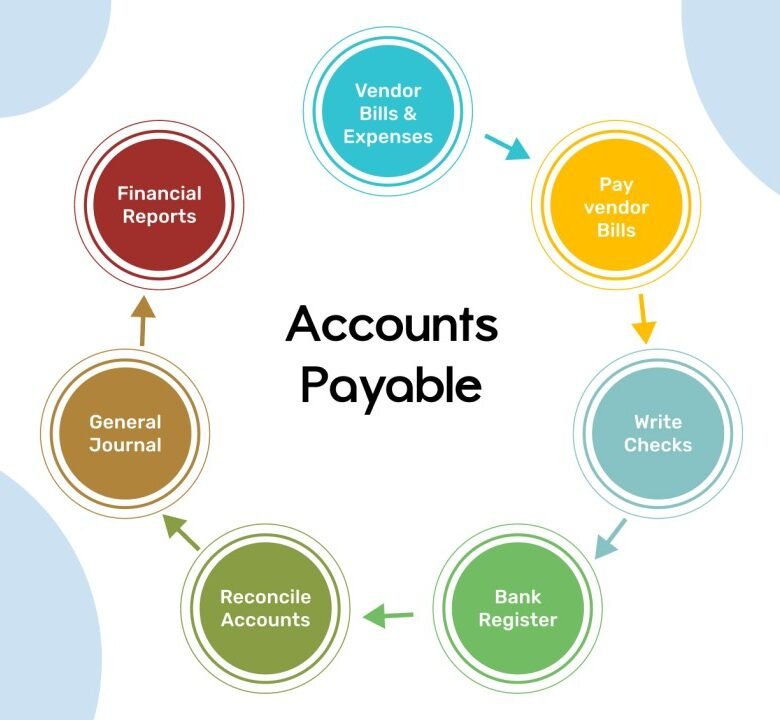
3. Core Stages of the Accounts Payable Approval Workflow
3.1 Invoice Capture
Invoices arrive via email, portals, or EDI (Electronic Data Interchange). Automated OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tools scan invoice details like supplier name, invoice number, tax amount, and due date.
3.2 Validation and Matching
Each invoice undergoes two-way or three-way matching:
-
Two-Way Match: Compares invoice with purchase order.
-
Three-Way Match: Compares invoice, purchase order, and goods receipt note (GRN).
This validation confirms that the supplier delivered the right goods at the agreed price.
3.3 Approval Routing
Invoices move through approval hierarchies based on value thresholds. A department head might approve invoices under $5,000, while the finance director handles higher-value approvals.
Automated workflows ensure proper segregation of duties and eliminate unauthorized approvals.
3.4 Payment Authorization
Once approved, the invoice is queued for payment through ACH, wire transfer, or check. Payment authorization follows treasury policy and internal control frameworks like COSO or SOX Section 404.
4. Why the Approval Process Matters
The accounts payable approval process ensures:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Aligns with IFRS, GAAP, and tax regulations.
-
Fraud Prevention: Stops fictitious vendors and inflated invoices.
-
Cost Savings: Identifies early-payment discounts and avoids late fees.
-
Audit Readiness: Maintains verifiable digital records for every transaction.
-
Supplier Trust: Builds reliable relationships through timely and accurate payments.
5. Technology in Modern AP Approval Systems
5.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI models recognize invoice patterns, detect anomalies, and route approvals intelligently. They flag duplicates or unusual payment amounts.
5.2 Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA bots replicate manual data-entry tasks such as invoice posting, reducing processing time by up to 80%.
5.3 Machine Learning (ML)
ML algorithms learn from past approval behaviors to predict optimal approvers or identify workflow bottlenecks.
5.4 Cloud-Based Platforms
Tools like SAP Concur, Bill.com, Airbase, and Tipalti enable global, paperless invoice approval with built-in analytics and mobile accessibility.
6. Roles and Responsibilities in the Approval Process
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Accounts Payable Clerk | Captures invoices, checks data accuracy, and initiates workflow. |
| Department Manager | Validates expenses related to departmental budgets. |
| Finance Controller | Reviews high-value invoices for financial accuracy. |
| Procurement Officer | Confirms purchase orders and contract compliance. |
| Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | Authorizes final payments above threshold limits. |
| Auditor | Ensures process adherence and verifies documentation. |
7. Step-by-Step Workflow Example
-
Invoice Submission: Vendor submits invoice via email or supplier portal.
-
Data Extraction: OCR captures invoice details into ERP.
-
Purchase Order Match: System validates against purchase order.
-
Approval Routing: Invoice sent to respective department for review.
-
Compliance Verification: System checks tax codes and budget limits.
-
Payment Authorization: CFO or controller approves disbursement.
-
Record Posting: Payment recorded in the general ledger (GL).
-
Audit Storage: All actions logged in the audit trail for compliance.
8. Common Challenges in AP Approval
-
Manual Data Entry Errors – Increases risk of duplicate payments.
-
Invoice Backlogs – Caused by paper-based or email-based submissions.
-
Policy Non-Compliance – Occurs when thresholds or approval limits are unclear.
-
Lack of Visibility – No real-time tracking for pending approvals.
-
Supplier Disputes – Stemming from delayed or incorrect payments.
9. Benefits of a Digitized Accounts Payable Approval Process
-
Faster Processing: Automated approvals reduce cycle time by up to 65%.
-
Cost Efficiency: Paperless workflows eliminate printing and storage costs.
-
Enhanced Accuracy: Systemic matching ensures only valid invoices are paid.
-
Improved Supplier Relations: Vendors gain transparency through portals.
-
Better Compliance: Centralized records ease audits and legal checks.
10. Best Practices for a Seamless Approval Workflow
-
Standardize Policies: Define approval limits and escalation paths.
-
Adopt Automation Tools: Use RPA and AI-enabled invoice management.
-
Regular Vendor Audits: Validate supplier data quarterly.
-
Integrate ERP Systems: Synchronize AP modules with procurement.
-
Monitor Metrics: Track key KPIs like invoice cycle time and cost per invoice.
11. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
| KPI | Definition | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Invoice Cycle Time | Time from receipt to payment approval. | ≤ 5 Days |
| First-Pass Yield Rate | Percentage of invoices processed without rework. | ≥ 90% |
| Cost per Invoice | Average processing cost per invoice. | ≤ $3 |
| Exception Rate | Invoices needing manual intervention. | ≤ 5% |
| Duplicate Payment Rate | Frequency of repeated payments. | 0% |
12. Risk Controls in the Accounts Payable Process
-
Segregation of Duties: No single person handles both approval and payment.
-
Approval Thresholds: Payments exceeding limits require higher authorization.
-
Audit Trails: Every approval action logged with time and user ID.
-
Vendor Verification: Periodic screening against sanctioned lists.
-
Access Controls: Role-based authentication prevents unauthorized entry.
13. How to Automate the AP Approval Process
To automate the accounts payable approval process:
-
Select an AP Automation Tool (e.g., Coupa, Stampli, or Basware).
-
Integrate with ERP such as Oracle or SAP for unified data.
-
Digitize Invoice Intake using OCR and eInvoicing.
-
Configure Approval Workflows with value-based rules.
-
Activate Notifications and Escalations to avoid delays.
-
Implement Analytics Dashboards for real-time tracking.
Automation ensures compliance, reduces human error, and delivers real-time visibility.
14. Compliance Frameworks Relevant to AP Approval
-
SOX (Sarbanes–Oxley Act) – Mandates documentation and internal controls.
-
IFRS & GAAP – Define global accounting and reporting standards.
-
GDPR – Governs vendor data privacy and consent.
-
AML Regulations – Prevent fraudulent supplier transactions.
-
ISO 27001 – Ensures information security during payment processing.
15. Future Trends in Accounts Payable Approvals
-
AI-Driven Predictive Approvals: Forecast bottlenecks and reassign tasks.
-
Blockchain-Based Audit Trails: Immutable transaction records.
-
Dynamic Discounting Models: Real-time supplier negotiation via portals.
-
Touchless Invoice Processing: 100% automated end-to-end workflow.
-
Embedded Finance Integration: Direct bank connections via APIs.
16. Sample Accounts Payable Approval Policy Template
| Policy Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Define standardized invoice approval framework. |
| Scope | Applies to all departments and vendors. |
| Approval Limits | Department Manager: ≤ $10K, CFO: > $10K. |
| Documentation | Digital invoice, PO, and GRN mandatory. |
| Audit Review | Quarterly verification by internal audit. |
| Retention Period | Records stored for 7 fiscal years. |
17. Case Study: Streamlining AP at a Mid-Sized Enterprise
A U.S. manufacturing firm processing 20,000 invoices annually implemented an AI-enabled approval platform.
Results after 6 months:
-
Invoice cycle time reduced from 14 days to 4 days.
-
Payment errors dropped by 95%.
-
Annual savings of $180,000 in operational costs.
-
Audit compliance score improved from 78% to 99%.
18. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the accounts payable approval process?
It is the system for verifying, approving, and paying supplier invoices after confirming accuracy, legitimacy, and compliance.
Q2: Why is the AP approval process important?
It prevents fraud, ensures compliance, improves financial control, and maintains trust with vendors.
Q3: What is a three-way match in AP?
A three-way match compares the purchase order, goods receipt, and invoice to confirm that the delivery and amount are valid before approval.
Q4: How can automation improve AP approvals?
Automation reduces manual work, eliminates errors, speeds up approvals, and ensures real-time audit visibility.
Q5: What tools are used for AP approval automation?
Popular tools include Tipalti, AvidXchange, Stampli, Airbase, and SAP Concur.
Q6: How long does an invoice approval take?
Industry benchmarks show 3–5 days for automated systems versus 10–14 days for manual processes.
Q7: Who approves invoices in an organization?
Approvals depend on the hierarchy—department managers, finance controllers, or the CFO, depending on the amount.
Q8: What compliance laws govern AP processes?
Major frameworks include SOX, IFRS, GAAP, GDPR, and AML regulations.
Learn More: What Is Single Instance Storage: Complete Technical Insight
The Ultimate Guide to the Store SWGOH: Unlock Rewards, Deals, and Strategies
19. Conclusion
A well-structured accounts payable approval process is not just an accounting necessity it’s a strategic tool for financial integrity and efficiency.
By combining automation, compliance frameworks, and analytics, organizations can achieve faster payments, lower costs, and complete transparency.